Inguinal Hernia
Introduction
An inguinal hernia occurs when intra-abdominal tissue pushes through a weak spot in the groin muscle. This causes a bulge in the groin or scrotum. The bulge may hurt or burn.
Causes of an inguinal hernia:
Most inguinal hernias occur because an opening in the muscle wall does not close as it should before birth. That leaves a weak area in the abdominal wall. Pressure on that area can cause tissue to push through and bulge out. A hernia can occur soon after the birth or much later in life.
The possibility of hernia increases if you are overweight or you do a lot of lifting, coughing, or straining. Hernias are more common in men than women. A woman may get a hernia during pregnancy because of the pressure on the abdominal wall.
In some cases, if the hernia does not cause much trouble, patient can possibly wait to have surgery.
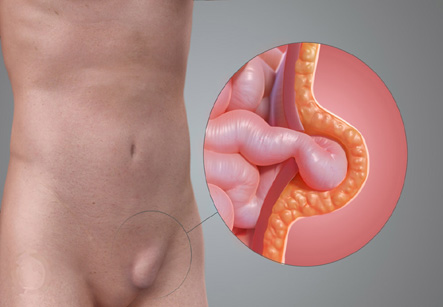
Indirect inguinal hernias
An indirect inguinal hernia is located in the inguinal canal. In males, this is the location of the spermatic cord.
Typically, this hernia is discovered when it descends into the scrotum.
Indirect hernia may be present at birth.
The treatment for this type of hernia is removal by surgery. Although this can be performed immediately after birth, some surgeons recommend a waiting period until the child has reached the age of two. Surgery is also the standard treatment for older children and adults.
Direct inguinal hernias
This type of hernia appears in adult life.
It is often two-sided or bilateral.
Obesity and hard physical work are risk factors for development of this hernia.
It can be seen and felt towards the middle of the inguinal ligament.
Surgery is the standard treatment for this type of hernia. Unfortunately, in many cases the hernia recurs and the surgery has to be repeated.
In case of a very elderly person having this hernia, the doctors may decide not to operate if the hernia is unlikely to cause complications.
Femoral hernias
Femoral hernias are very rare, and mostly seen in middle-aged and elderly obese women who have given birth several times.
The hernia is seen as a lump below the inguinal ligament.
The treatment of choice is surgery.
Symptoms:
The main symptom of an inguinal hernia is a bulge in the groin or scrotum. Hernia often feels like a round lump. The bulge may form over a period of weeks or months. It can also appear all of a sudden after lifting heavy weights, coughing, bending, straining, or laughing. The hernia may be painful, but some hernias cause a bulge without pain.
There may be swelling and a feeling of heaviness, tugging, or burning in the area of the hernia. These symptoms may get better after lying down. The inguinal hernia can be pressed back in the abdomen or it reduces on its own after lying down.
Sudden pain, nausea, and vomiting are signs strangulation, which means that a part of intestine may have become trapped in the hernia. Call the doctor immediately if you have a hernia and have these symptoms.
Diagnosis:
A doctor can usually diagnose a hernia based on the symptoms and a physical exam. The bulge is usually easy to feel.
Treatment:
If there is inguinal hernia in the patient, it will not heal on its own. Surgery is the only way to treat a hernia.
In some cases, if the hernia does not cause much trouble, patient can possibly wait to have surgery. The hernia may get worse, but it may not. In some cases, very small and painless hernias may never need to be repaired.
Most people with hernias have surgery to repair them, even in absence of any symptoms. This is because many doctors believe that surgery is less dangerous than impending risk of strangulation.
However, there is no need of an emergency surgery for this hernia. If the hernia is small and painless and it can be pushed back into the belly; patient may be able to wait.
Babies and young children are more likely to have tissue get trapped in a hernia. Hence, for a child having a hernia, a surgery is needed to repair it.
A hernia may come back after surgery. To reduce the chance of recurrence, stay at a healthy weight. Do not smoke, avoid heavy lifting, and try not to push hard while having a bowel movement or passing urine.
Risk factors for inguinal Hernia:
A hernia can develop in anyone, from a newborn baby to a senior citizen. The following may increase the risk of a hernia by increasing pressure on the abdominal wall:
1. Chronic cough, such as smoker’s cough
2. Obesity
3. Straining during bowel movements or while urinating
4. Pregnancy
5. Lifting heavy objects
6. Persistent sneezing, such as that caused by allergy